Syncytia formation and syncytiotrophoblast function
syncytia: highly multinucleated structures.
not all cell fusion will lead to syncytia
syncytia is one of the models to study cell-cell fusion
among others like gametes fusion and virus (covid-19) invading
virus induced cell-cell fusion implicates the human syncytialtrophoblast formation
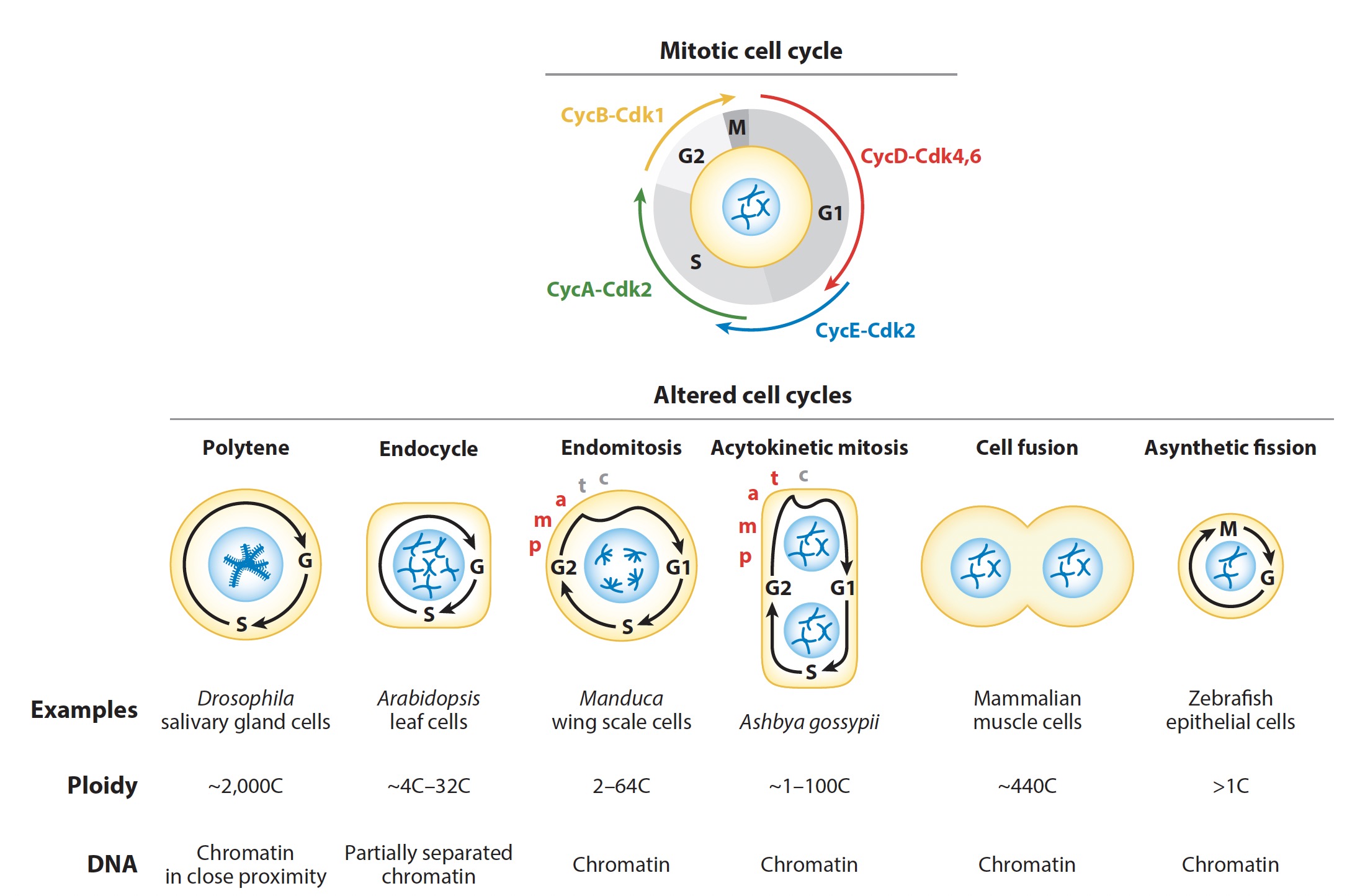
Syncytia in life/biology
- human syncytiatrophoblasts form with a cell-cell fusion strategy
- mouse TGCs are from endocycle
- highly multinucleated
- density calculation:
- cell mass? cell volume?
| Cell type (species) | Organ system | Predominant nuclear number and ploidy per nucleus (C) | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germline cyst (female mouse) | Reproductive | Up to 25 × 1C | Incomplete cytokinesis | Lei and Spradling 2016 |
| Germline cyst (female fruit fly) | Reproductive | 16 × 1C | Incomplete cytokinesis | Lei and Spradling 2016 |
| Cardiomyocyte (pig) | Cardiovascular | 8 × 2C | Incomplete cytokinesis | Velayutham et al. 2020 |
| Cardiomyocyte (mouse) | Cardiovascular | 2 × 2C | Incomplete cytokinesis | Soonpaa et al. 1996 |
| Cardiomyocyte (human) | Cardiovascular | 1 × 4C and 2 × 2C | Incomplete cytokinesis or endocycle | Brodsky et al. 1992; Hesse et al. 2012; Mollova et al. 2013; Bergmann et al. 2015 |
| Osteoclast (chicken) | Skeletal | 4 × 2C | Cell–cell fusion | Piper et al. 1992 |
| Macrophage granuloma (human) | Lymphatic | 2 × 2C and 1 × 4C | Incomplete cytokinesis or endocycle | Herrtwich et al. 2016 |
| Myocyte (mouse) | Muscular | ~ 220 × 2C (extensor digitorum longus) | Cell–cell fusion | Hansson et al. 2020 |
| Myocyte (fruit fly) | Muscular | 10–15 × 32C (ventral longitudinal muscles 3 and 4) | Cell–cell fusion, endocycle | Windner et al. 2019 |
| Megakaryocyte (human, rat) | Cardiovascular | 1 × 8C, 1 × 16C, 1 × 32C | Incomplete cytokinesis and incomplete karyokinesis | Odell et al. 1976; Brown et al. 1997; Lordier et al. 2008 |
| Hepatocyte (human) | Digestive | 1 × 2C, 2 × 2C, 2 × 4C, 1 × 4C, 1 × 8C | Incomplete cytokinesis or endocycle | Kudryavtsev et al. 1993 |
| Rectal papillar cells (fruit fly) | Digestive | 100 × 8C | Endocycle, cytoplasm-sharing | Fox et al. 2010; Schoenfelder et al. 2014; Peterson et al. 2020 |
| Syncytiotrophoblast (human) | Extraembryonic | up to 6 × 10^10 × 2C | Cell–cell fusion | Simpson et al. 1992 |
| Trophoblast giant cells (mouse) | Extraembryonic | Up to 1 × 512–1024C | Endocycle | Barlow and Sherman 1972; MacAuley et al. 1998 |
| Salivary gland (fruit fly) | Digestive | 1 × 512–1024C | Endocycle | Hammond and Laird 1985 |
| Subperineurial glia (fruit fly) | Nervous | 1–4 × 4–32C | Incomplete cytokinesis or endocycle | Unhavaithaya and Orr-Weaver 2012; Von Stetina et al. 2018 |
- Triggers
- ligand-receptor signaling
- mechanical signaling
- Properties
- nuclei-cytoplasmic ratio
- in response to physiological demands
control the avaliability of cell cycle regulators- limit biosynthetic capacity
- cell size
with cell fusion, given a certain cell volume, the surface area decreases, so that:
~ -nutritent uptake efficiency ~ -metabolic rate
- nuclei-cytoplasmic ratio
- nucleocytoplasmic transport
- drives osmotic shifts to regulate the volume of both compartments
- Functions
Questions from this investigation
- single cell profiling: transcripts/protein concentration (density from spatial sequencing) scales (super-, scale, or sub-) (to nuclei/DNA contents) in syncytiatrophoblasts compare to early syncytiatrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts.
- single nuclei profiling: transcripts abundance per nuclei scales (super-, scale, or sub-) to number of nulei in a cell.