Placenta Pathologies to look for
Villouse Maldevelopment
Three types of maldevelopment:
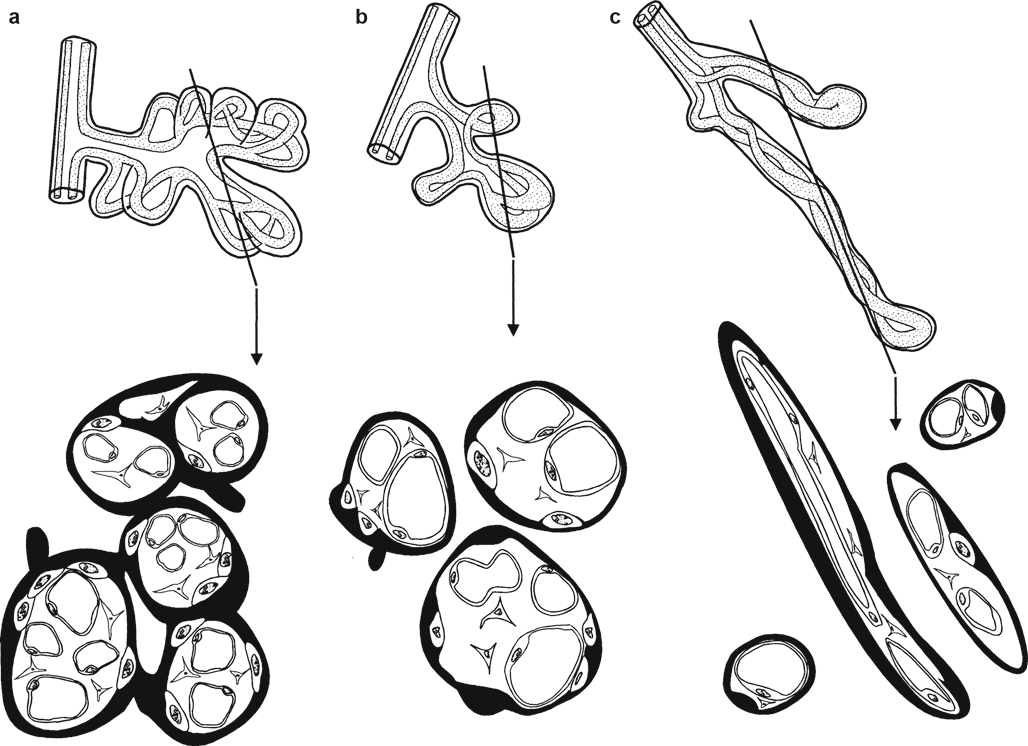
Examples
- immature intermediate villi in term placentas. a) normal. b) more homogeneously distributed immature intermediate villi
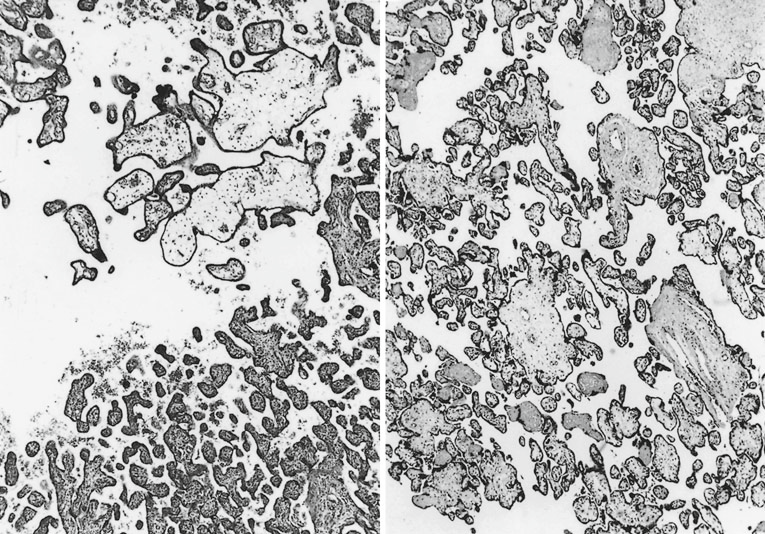
- The chronic preplacental hypoxia causes prevalence of branching angiogenesis, resulting in multiply branched and indented terminal villi. a) x120 intense trophoblastic knotting as a result of increased b) x300 artifactual syncytial knotting and bridging
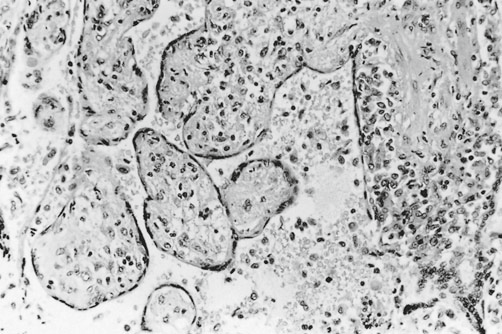
 conglomeration of terminal villi with apparent syncytial “bridging” and “sprouting” artifactually, caused by tangential sectioning.
conglomeration of terminal villi with apparent syncytial “bridging” and “sprouting” artifactually, caused by tangential sectioning.
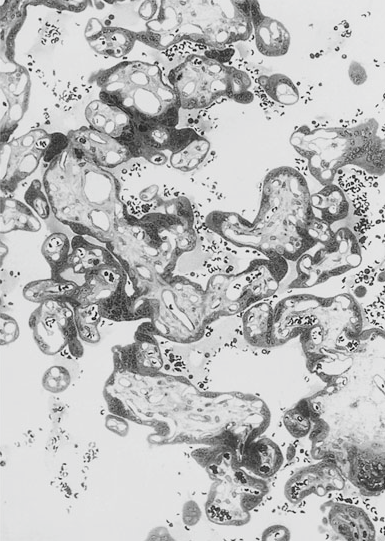
- IUGR and postplacental hypoxia
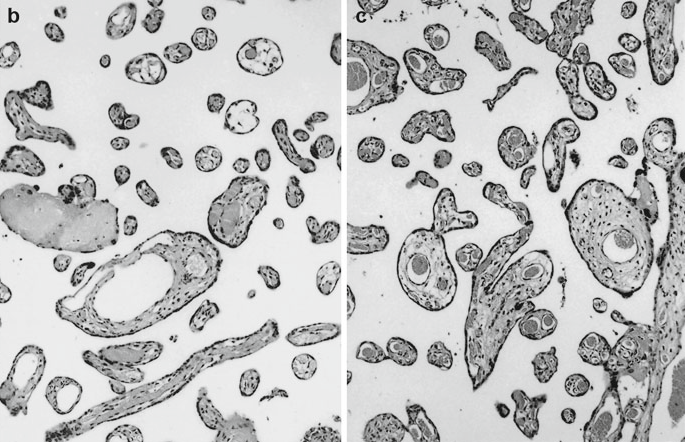
Hispathological approach to Villous alteration
- Villi development
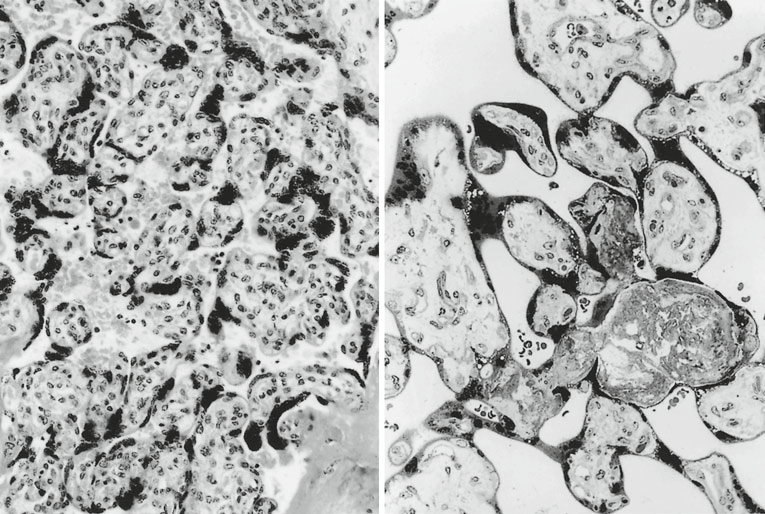
- accelerated
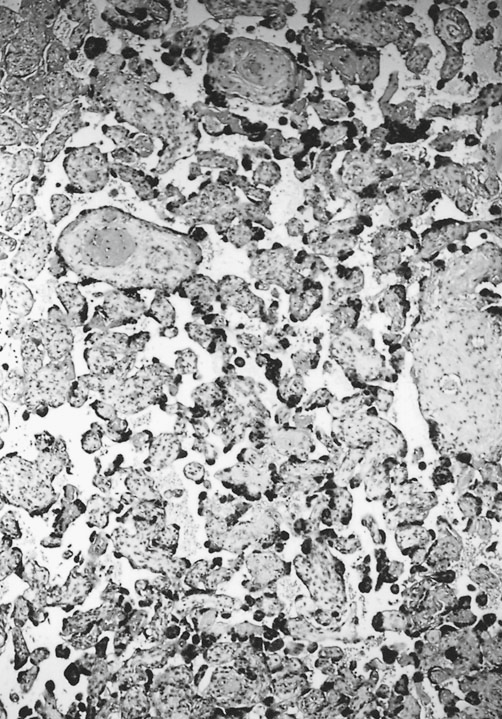
- accelerated maturity ( at left ) with numerous syncytial knots associated with small terminal villi and large immature intermediate villi at the right
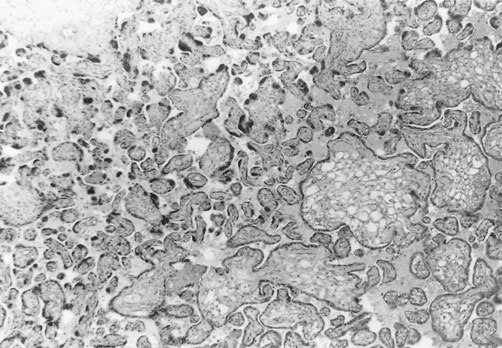
- inflammation
- chorangiosis
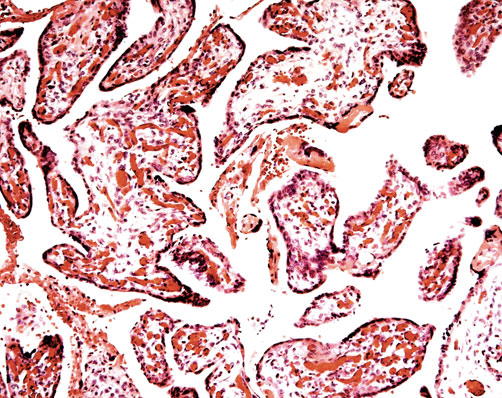
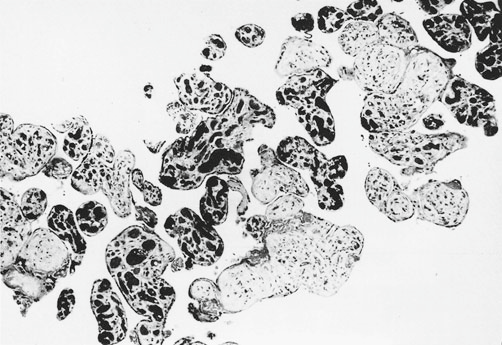
- fibrosis
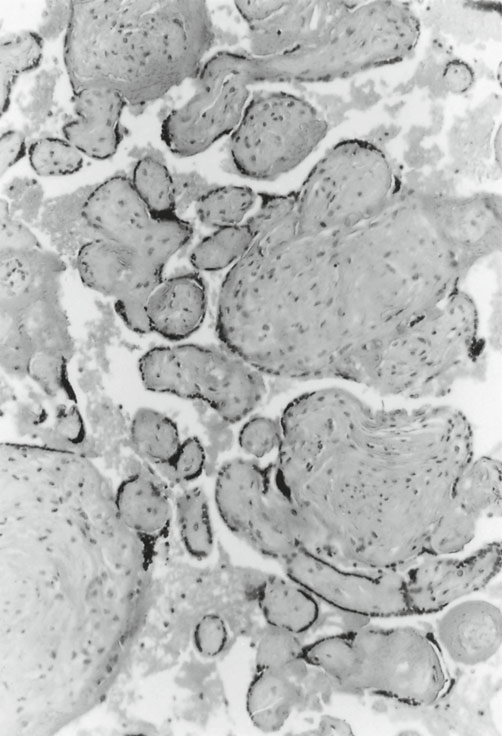
- large Hofbaucer cells in the edematous villus
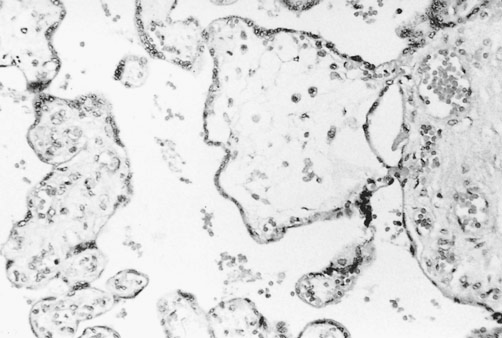
- destroyed hofbaucer cells: The villi exhibit partly normal immature reticular stroma with an abundance of macrophages (Hofbauer cells, dark cells in reticular spaces), which is normal for immature intermediate villi. In other villi, the reticular pattern is partially destroyed by various degrees of edema.
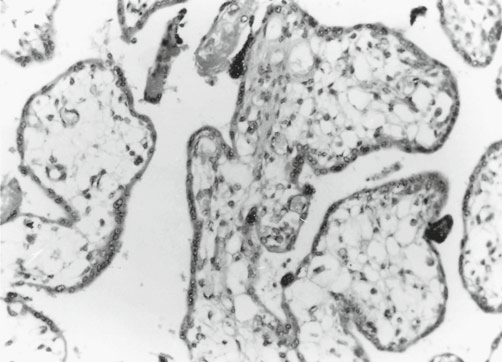
- infiltration of chronic in fl ammatory cells